本文介绍三篇点云相关的综述文章,并作归纳分析。[1] 的目录结构为:
- 3D Shape Classification
- Multi-view based Methods
- Volumetric-based Methods
- Point-based Methods
- Pointwise MLP Methods
- Convolution-based Methods
- Graph-based Methods
- Hierarchical Data Structure-based Methods
- Other Methods
- 3D Object Detection and Tracking
- 3D Object Detection
- Region Proposal-based Methods
- Single Shot Methods
- 3D Object Tracking
- 3D Scene Flow Estimation
- 3D Object Detection
- 3D Point Cloud Segmentation
- 3D Semantic Segmentation
- Projection-based Methods
- Discretization-based Methods
- Hybrid Methods
- Point-based Methods
- Instance Segmentation
- Proposal-based Methods
- Proposal-free Methods
- Part Segmentation
- 3D Semantic Segmentation
[2] 的目录结构为:
- Classification
- Projection-based Methods
- Multi-view Representation
- Volumetric Representation
- Basis Point Set
- Point-based Methods
- MLP Networks
- Convolutional Networks
- Graph Networks
- Other Networks
- Projection-based Methods
- Segmentation
- Semantic Segmentation
- Projection-based Methods
- Point-based Methods
- Instance Segmentation
- Proposal-based Methods
- Proposal-free Methods
- Semantic Segmentation
- Detection, Tracking and Flow Estimation
- Object Detection
- Projection-based Methods
- Point-based Methods
- Multi-view Methods
- Object Tracking
- Scene Flow Estimation
- Object Detection
- Registration
- Traditional Methods
- Learning-based Methods
- Augmentation and Completion
- Discriminative Methods
- Generative Methods
[3] 只分析了 Segmentation 和 Detection 任务,每个任务都从 Point-based,Voxel-based,View-based 三种方法来阐述。
本文结合这三篇综述,对不同任务的不同方法作详尽的归纳。
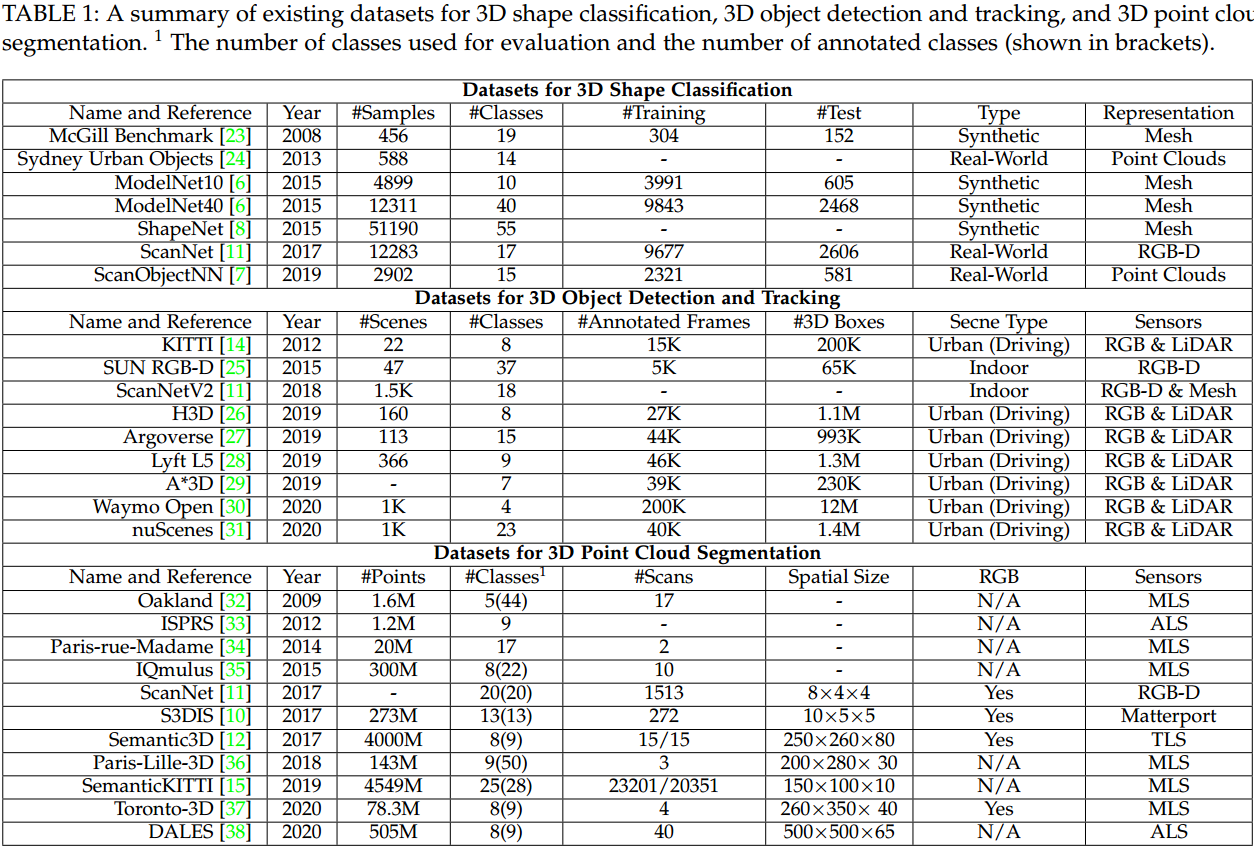
1. Datasets
2. Metrics
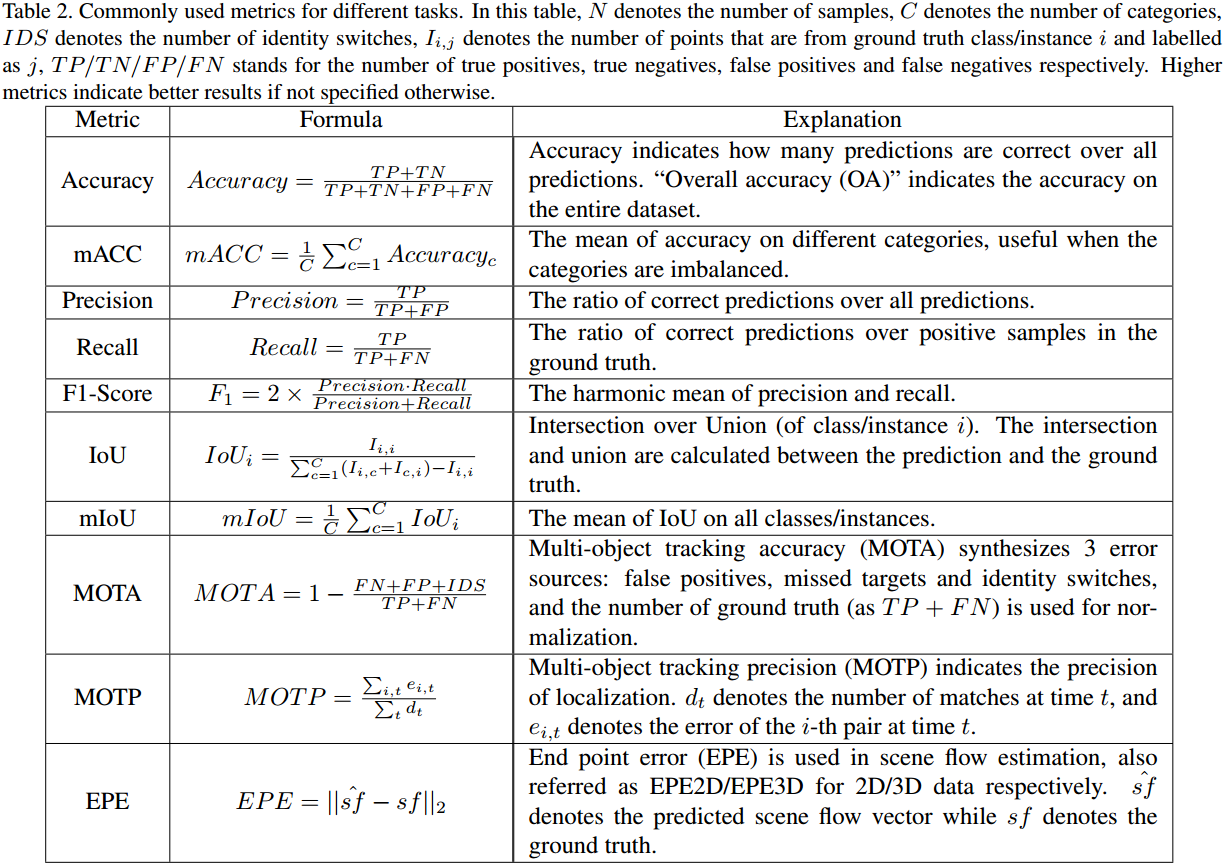 不同任务的主要度量指标如图 2. 所示,此外还有:
不同任务的主要度量指标如图 2. 所示,此外还有:
- Average Precision(AP)
用于 3D 目标检测,计算的是 precision-recall 曲线下的面积:\(AP=\frac{1}{11}\sum _ {r\in\{0,0.1,...,1\}}\mathop{\max}\limits _ {\tilde{r} : \tilde{r}\geq r} p(\tilde{r})\),其中 \(r\) 表示 recall,\(p(r)\) 表示对应的 precision。 - Average Orientation Similarity(AOS)
类似的,\(AOS=\frac{1}{11}\sum _ {r\in\{0,0.1,...,1\}}\mathop{\max}\limits _ {\tilde{r} : \tilde{r}\geq r} s(\tilde{r})\)。 - Panoptic Quality(PQ)[4]
用于全景分割,可分解为 Segmentation Quality(SQ) 以及 Recognition Quality(RQ),即同时评估语义分割及 Instance 分割,定义为: \[\begin{align} PQ &= \frac{\sum _ {(p,g)\in TP}IoU(p,g)}{\vert TP\vert+\frac{1}{2}\vert FP\vert+\frac{1}{2}\vert FN\vert} \\ &= \frac{\sum _ {(p,g)\in TP}IoU(p,g)}{\vert TP\vert} \times\frac{\vert TP\vert}{\vert TP\vert+\frac{1}{2}\vert FP\vert+\frac{1}{2}\vert FN\vert} \\ &= SQ \times RQ \tag{1} \end{align}\] \(RQ\) 就相当于 F1-Score,只不过这里的 TP 可能是根据点集交并比来判断的。
3. Classification
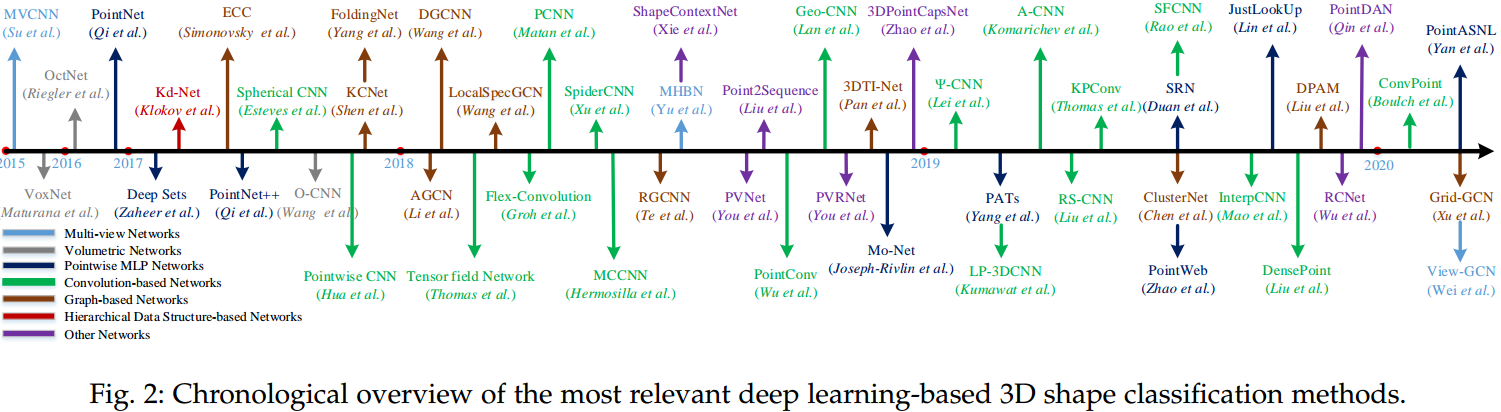 分类是最基础的任务,创新的网络结构基本首先在分类任务中进行应用,网络结构的创新目的本质上又是更有效的特征提取。PointCloud Feature Extraction 中已经较详细的描述了基于点的点云特征提取的相关进展,如图 3. 所示,所有高层任务所用到的网络结构基本可以在这找到对应的基础网络。
分类是最基础的任务,创新的网络结构基本首先在分类任务中进行应用,网络结构的创新目的本质上又是更有效的特征提取。PointCloud Feature Extraction 中已经较详细的描述了基于点的点云特征提取的相关进展,如图 3. 所示,所有高层任务所用到的网络结构基本可以在这找到对应的基础网络。
3.1. Multi-view based Methods
这种方法将点云投影到特定的几种视角平面上,提取特征后再将各个视角的特征进行整合,最后得到全局特征,来作分类。一般选取 Bird-eye View 与 Front View 两个视角,BV 的好处是目标尺寸的一致性,FV 的好处是对狭长型目标较为友好。代表方法由 MVCNN,MHBN,View-GCN 等。
3.2. Volumetric-based Methods
这种方法将点云量化为 3D 体素(Voxel),然后采用 3D 卷积作特征提取。方法有 VoxNet,OctNet,O-CNN 等。
3.3. Point-based Methods
此类方法玩法较多,因为直接在原始点云上进行特征提取,所以没有额外的信息损失。其研究的变种也较多。
3.3.1. Pointwise MLP Methods
典型代表为 PointNet,直接对每个点的特征维度进行 MLP 变换,然后用 Symmetric Operator 在点的维度进行 Reduction 得到全局特征。此外可以加入各种采样策略,作特征的级联采样并提取,其它方法有 DeepSets,PointNet++,Mo-Net,PATs,PointWeb,SRN,JustLookUp,PointASNL 等。
3.3.2. Convolution-based Methods
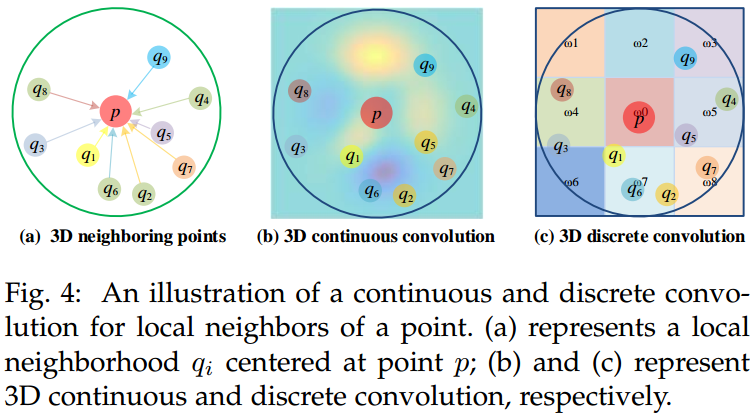 由于点云数据的离散性,传统的图像 2D/3D 卷积无法直接使用。如图 4. 所示,根据卷积核的定义方式,基于点的卷积可分为 Continuous Convolution 和 Discrete Convolution。
由于点云数据的离散性,传统的图像 2D/3D 卷积无法直接使用。如图 4. 所示,根据卷积核的定义方式,基于点的卷积可分为 Continuous Convolution 和 Discrete Convolution。
- Continuous Convotion
对于以某一中心点作卷积的点集,其卷积核权重是与点集相对该中心点的空间分布有关。权重,即空间分布的计算,一般通过 MLP 网络对每个点的欧式距离等特征编码得到。 - Discrete Convotion
对于以某一中心点作卷积的点集,其卷积核权重是与点集相对该中心点的空间残差有关。首先对点集区域以中心点作一定形状的栅格化,对每个栅格内的点进行特征提取,然后再以栅格为单位,作类似传统的卷积操作。
3.3.3. Graph-based Methods
该方法将点云中的点建模为图顶点,然后将相邻点进行有向连接得到有向图。点云的特征提取可在 Spatial 或 Spectral 空间内进行。
在 Spatial 空间,图顶点通常包含坐标值,反射率,颜色等初始特征,图边通常与连接边的两个顶点空间距离有关,一般通过 MLP 网络构建,Point-GNN 中比较详细得描述了这一过程。
在 Spectral 空间,卷积定义为光谱滤波器,用 Graph Laplacian Matrix 的特征向量相乘实现。
3.3.4. Hierarchical Data Structure-based Methods
该类方法将点云构建成级联的类树状结构,特征学习通过树叶至树根传递。代表方法有 OctNet,Kd-Net 等。
3.3.5. Other Methods
4. Detection and Tracking
4.1. 3D Object Detection
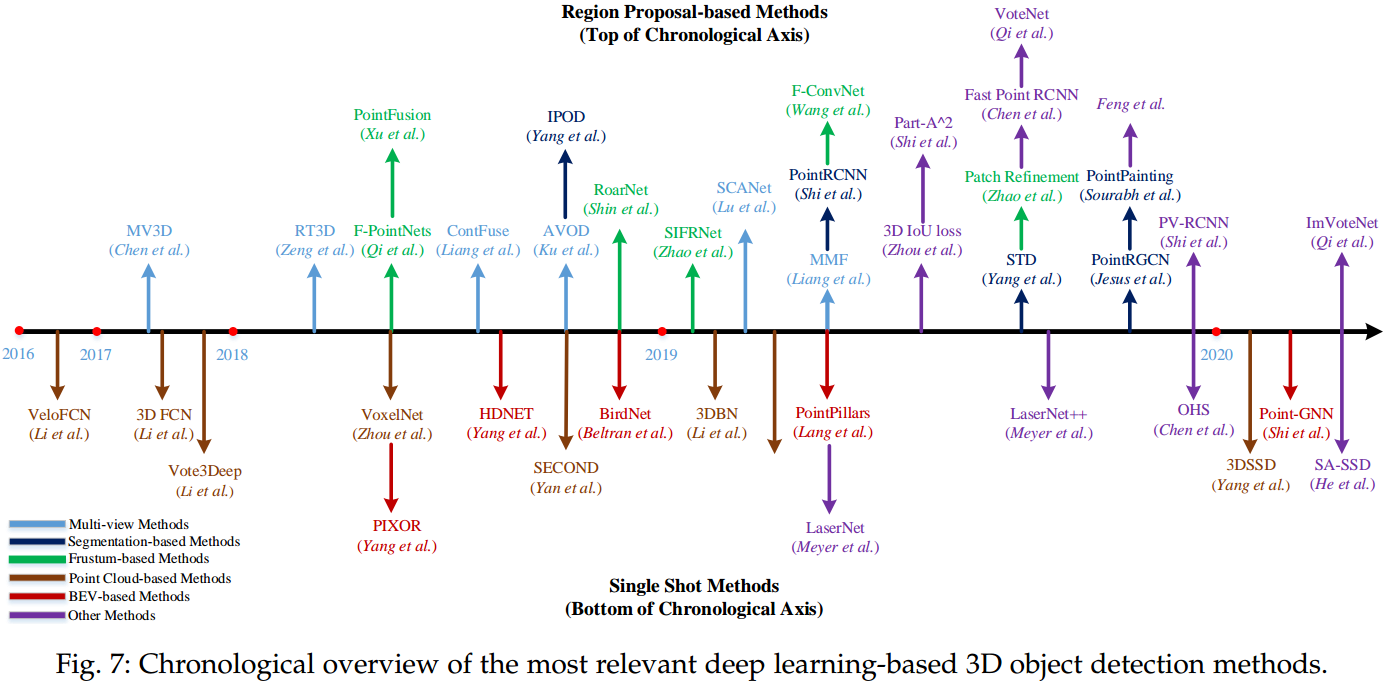
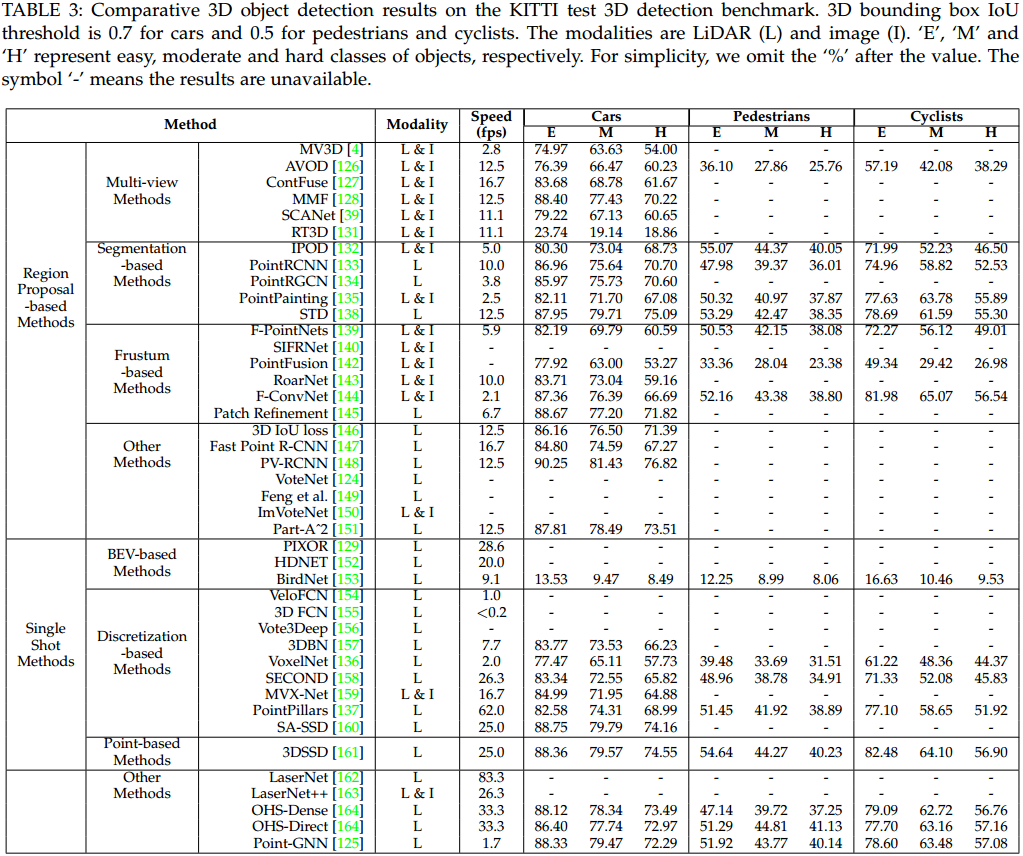 目标检测是非常重要的一个任务,不同类型的方法如图 5. 所示,其性能如图 6. 所示。
目标检测是非常重要的一个任务,不同类型的方法如图 5. 所示,其性能如图 6. 所示。
4.1.1. Region Proposal-based Methods
这种方法首先找出候选区域框,然后作进一步的目标属性精修。根据候选框的产生方式,可分为 Multi-view based Methods,Segmentation-based Methods 以及 Frustum-based Methods。
Multi-view based Methods 一般速度比较慢,会融合不同模态的数据,算法也比较复杂。
Segmentation-based Methods 先通过语义分割的方法去除背景区域点,根据前景点生成高质量的候选框集合,由较高的召回率,且善于处理遮挡等较为复杂的场景。
Frustum-based Methods 通常通过图像生成候选目标框,然后根据视锥去提取激光点云或毫米波点云的目标测量,对于中后期的融合,该方法应用也较多。
4.1.2. Single Shot Methods
单阶段方法没有提取候选框这个步骤,网络直接预测目标的 3D 属性,可分为 BEV-based,Discretization-based Methods,以及 Point-based Methods。
BEV-based Methods,Discretization-based Methods 均通过离散化点云空间,然后作类似图像的 2D 卷积或 3D 卷积操作。Point-based Methods 则直接在点云级别作特征提取以及目标检测。这些方法之前讨论较多了,不做展开。
4.2. 3D Object Tracking
相比图图像的 2D 跟踪,3D 跟踪能比较容易的解决遮挡,光照,尺度等问题。本博客讨论过基于传统 ICP 的 ADH-Tracker 方法,也介绍过基于深度学习的 P2B 方法。总体上来讲,3D 目标跟踪套路较少,除非将检测,跟踪,预测联合来优化,比如 PnPNet。
4.3. 3D Scene Flow Estimation
3D Scene Flow 问题定义为:给定 \(\mathcal{X,Y}\) 两个点云集,3D Scene Flow \(D=\{d _ i\} ^ N\) 描述了 \(\mathcal{X}\) 中的点 \(x _ i\) 与其在 \(\mathcal{Y}\) 中的最近对应点 \(x _ i '\) 的距离 \(x _ i '=x _ i+d _ i\)。
3D Scene Flow 是一个中低层任务,根据 3D Scene Flow 可以进一步作运动物体分割聚类,目标运动速度估计等高层任务。FlowNet3D 是较早采用深度学习进行 3D Scene Flow 估计的方法。类似图像中的光流估计,可采用无监督方法,对应的 Loss 有 EMD 等。
5. Segmentation
5.1. Semantic Segmentation
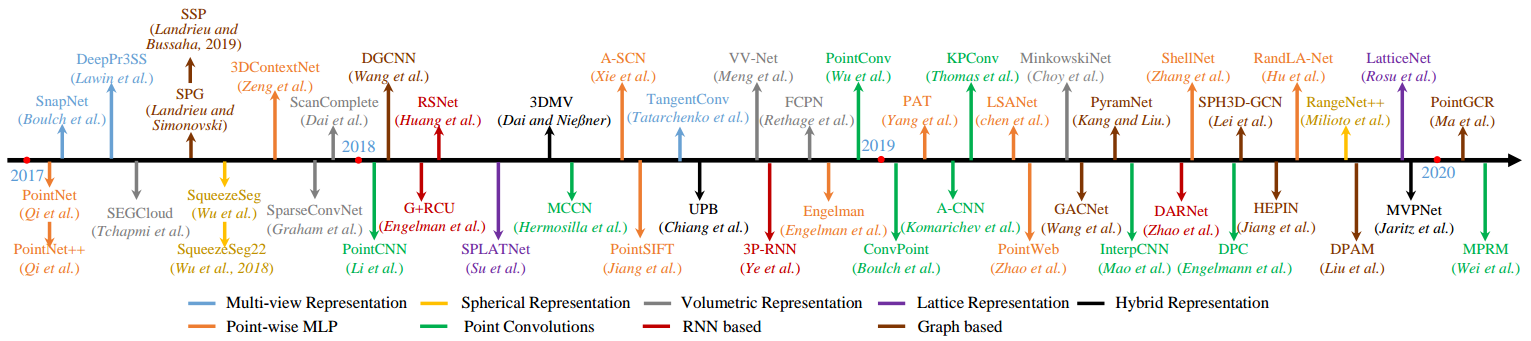
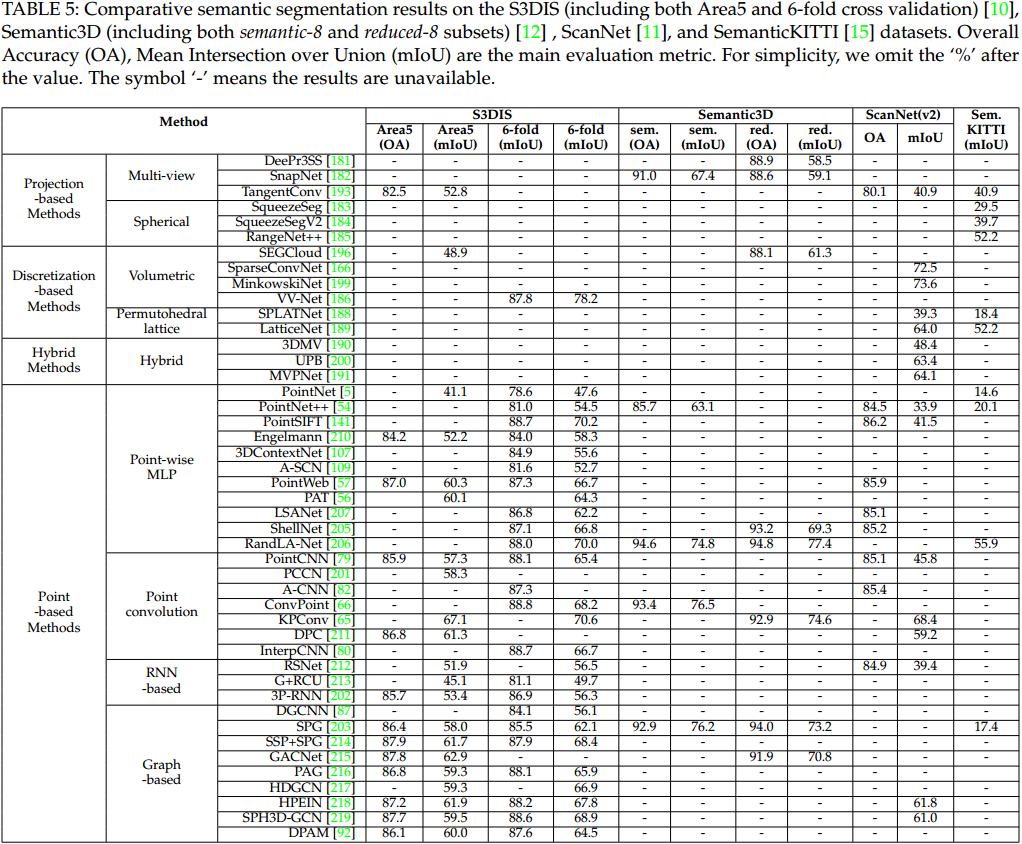 语义分割方法如图 7. 所示,各方法的性能如图 8. 所示。
语义分割方法如图 7. 所示,各方法的性能如图 8. 所示。
5.1.1. Projection-based Methods
点云语义分割需要尽可能保留点级别的特性信息,投影法基本上可分为 BirdView,Spherical,Cylinde 三种,代表方法有 PolarNet,RandLA-Net,Cylinder3D 等。
5.1.2. Discretization-based Methods
这种方法是将点云空间体素化,然后用 3D 卷积的形式来提取特征。一般会丢失点级别的信息,所以需要点级别的信息提取方式来辅助。
5.1.3. Point-based Methods
在点云语义分割中,点级别的特征提取是非常有必要的,一般采用点级别的 MLP,PointNet Convolution,RNN,Graph-based 等方法,本质上都是对每个点周围的点集作特征提取操作。PointCloud-Feature-Extraction 中有较详细的描述。
5.2. Instance Segmentation
 实例分割不仅作语义分割,还得将同一目标的点云作聚类处理。其可分为 Proposal-based Methods,以及 Proposal-free Methods。Proposal-based 将实例分割分解为目标检测以及实例 mask 预测两个任务;Proposal-free 则是自下而上的求解该问题,一般通过预测语义及聚类辅助量,最后通过相关聚类策略实现。相关方法如图 9. 所示。
实例分割不仅作语义分割,还得将同一目标的点云作聚类处理。其可分为 Proposal-based Methods,以及 Proposal-free Methods。Proposal-based 将实例分割分解为目标检测以及实例 mask 预测两个任务;Proposal-free 则是自下而上的求解该问题,一般通过预测语义及聚类辅助量,最后通过相关聚类策略实现。相关方法如图 9. 所示。
6. Registration
点云注册主要有两大块应用,本车的位姿估计以及目标车的速度估计。对于前后帧点云的注册能估计出前后帧时间内本车的位姿变化;对于目标点云的注册能测量出目标的速度。
传统的点云注册方法通过 ICP 实现,详见 Object Registration with Point Cloud 中的描述。对于两个点云集合,也可通过网络求解 \(R,t\)。
7. Augmentation and Completion
激光点云数据往往受噪声,离群点,未测量点影响,可以采用网络对点云进行噪声滤出处理,以及点云补全处理,这里不做展开。
8. Conclusion
基于点云的每个任务对应的方法,其实都可分为 View-based,Voxel-based,Point-based 三大类,当然也可以结合来做。其中 View-based 主要由 BirdView,Spherical,Cylinde 三种;Voxel-based 则主要分为 2D/3D;Point-based 则玩法较多,不过本质上还是对点周围的小点集作特征提取。
9. Reference
[1] Guo, Yulan, et al. "Deep learning for 3d point clouds: A survey." IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence (2020).
[2] Lu, Haoming, and Humphrey Shi. "Deep Learning for 3D Point Cloud Understanding: A Survey." arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.08920 (2020).
[3] Li, Ying, et al. "Deep learning for LiDAR point clouds in autonomous driving: a review." IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (2020).
